Complications associated with ureteral stents can be classified as intraoperative, early complications if they appear between 2 and 4 weeks after stenting, and late complications, depending on the time of onset of side effects. The most common side effects are the development of vesicoureteral reflux, LUTS and stent discomfort.. The prophylactic placement of ureteral stents during colorectal surgery may facilitate ureteral identification and/or recognition of injury. 1,2 However, reports have cautioned against routine use of ureteral stents owing to the potential of iatrogenic injury during insertion and postoperative complications, including stenosis and infection. 3,4 At present, no evidence-based guidelines exist.
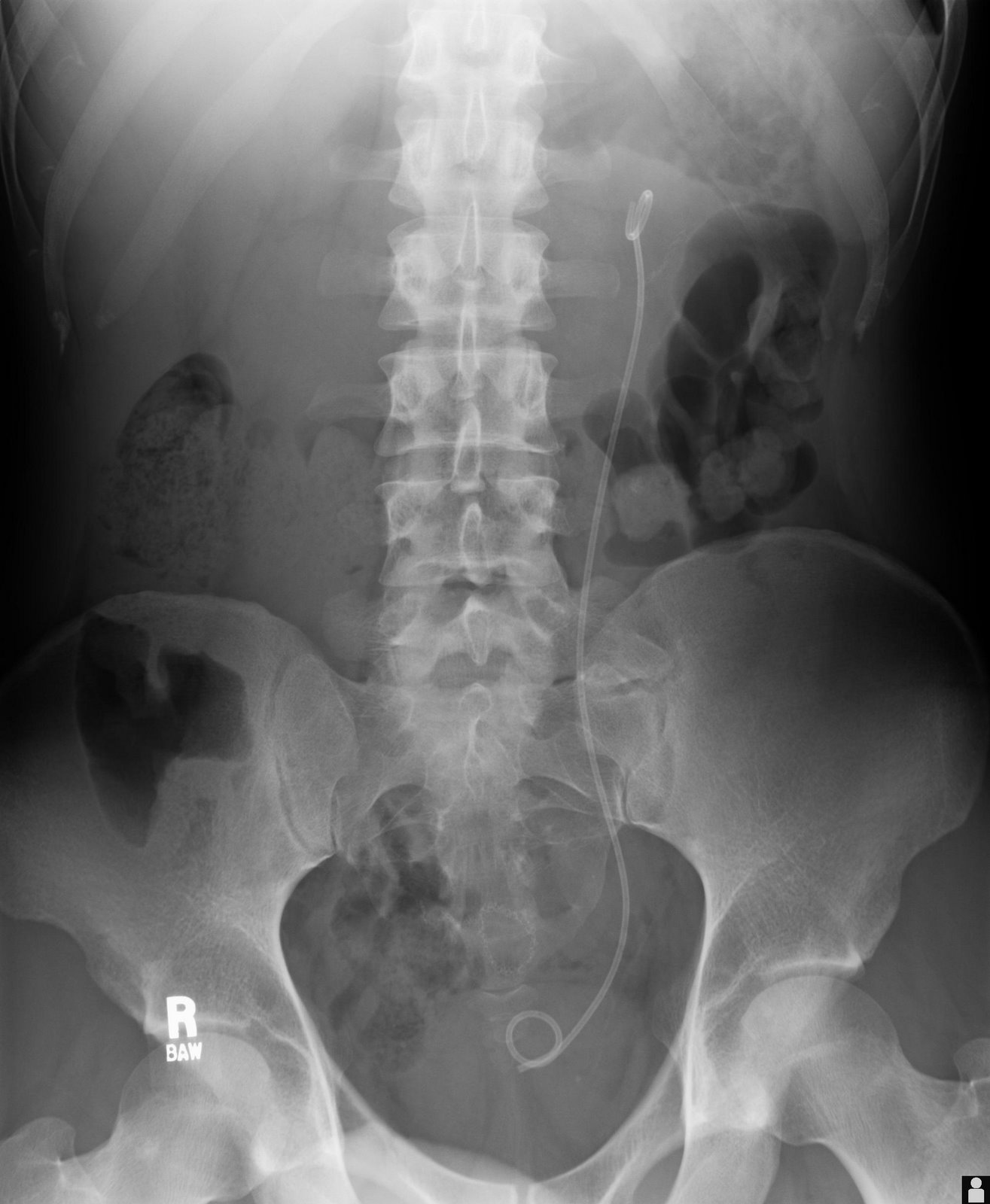
Abdominal Xray Interpretation (AXR) Radiology OSCE Geeky Medics
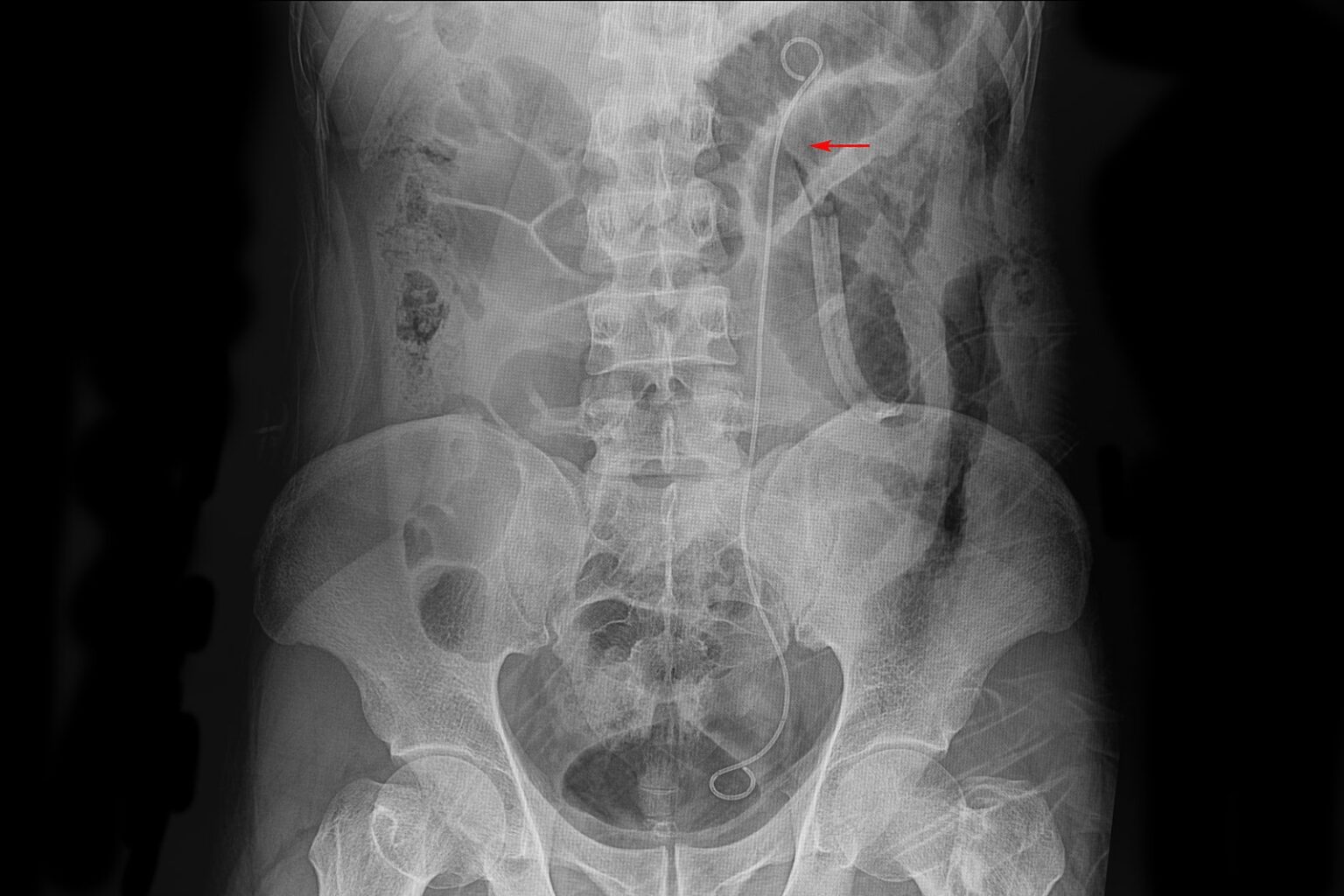
What to Expect from a Ureteral Stent Advanced Urology

Endourologic Management of an Iatrogenic Ureteral Avulsion Using a Thermoexpandable Nickel

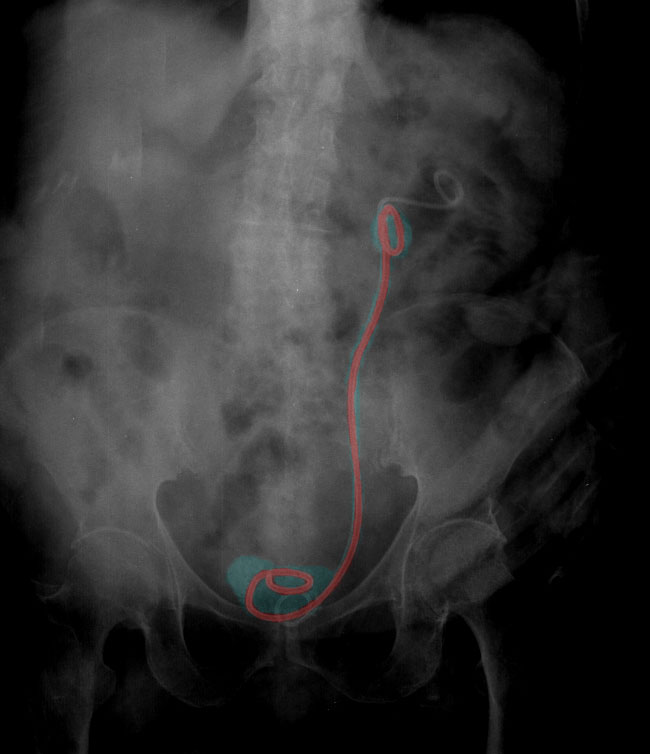
Complications of Ureteral Stent Placement RadioGraphics
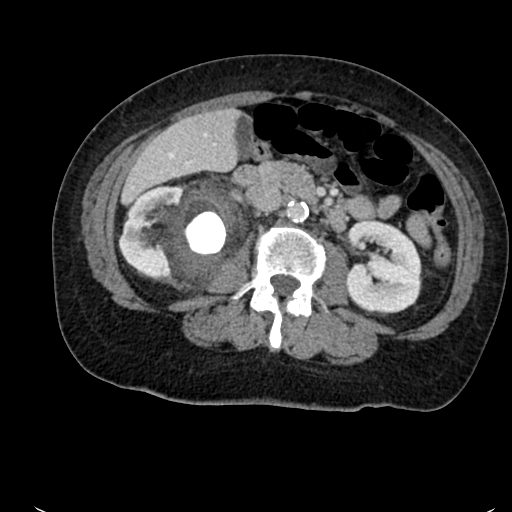
Pyelitis and ureteral stent encrustation Image

Ureteral stent placement Galvao Otoni INTERNALMEDICINE VCA Arboretum View

(PDF) Extensive Retroperitoneal Fibrosis with Duodenal and Ureteral Obstruction Associated with

Ureteroscopy ด้วย Laser Lithotripsy การรักษานิ่วในไต Khao Ban Muang

Figure 2 from Ureteral stent versus no ureteral stent for ureteroscopy in the management of

Clinical and prognostic factors associated with internal ureteral stent placement for

Medical Disposable 4.8 Fr Double J Ureteral Stent Set For Urology Surgery
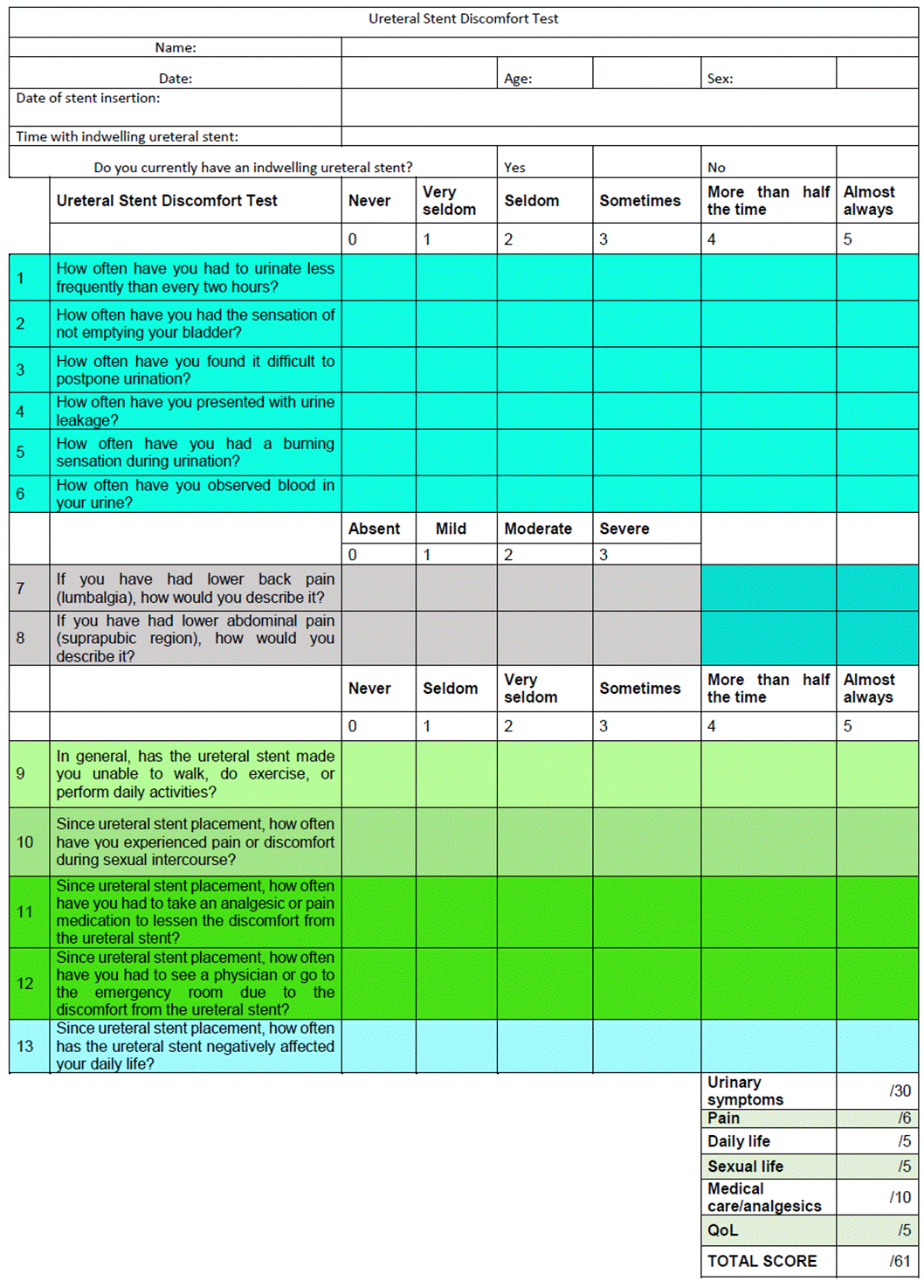
Development and validation of the Ureteral Stent Test (USDT). A simple, effective

Passive Ureteral Dilation Secondary to Ureteral Stenting and Biofilm Evaluation Formed on

Complications of Ureteral Stent Placement RadioGraphics
Medical Ureteral Stent Double J Pigtail Hydrophilic Coating Multi Loop Uro

(PDF) Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral

Medical Disposable 4.8 Fr Double J Ureteral Stent Set For Urology Surgery
How long is too long? "I that I had a ureteral stent"

PU Urology Surgical Instruments 48Fr DoubleJ Ureteral Stents

Sonographic appearance of an ureteral stent NephroPOCUS
Ureteral stents are thin, flexible tubes that hold ureters open. The ureters are part of the urinary system. Typically, these long, thin tubes carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Healthcare providers place ureteral stents to prevent or treat ureteral obstructions. Silicone or polyurethane (plastic) ureteral stents are about 10 to 15.. A bowel movement every other day is reasonable. Use stool softeners (i.e. Colace, Senekot, Fibercon, etc.) if needed.. We will then schedule an appointment to have your ureteral stent removed about 4-6 weeks after that. Take Control of Your Health. Book an appointment today and let one of our physicians examine your urological health. We are.